Increased robot deployment, such as in warehousing, has revealed a need for seamless collaboration among heterogeneous robot teams to resolve unforeseen conflicts.
To address this challenge, we propose a novel decentralized framework that enables robots to request and provide help.
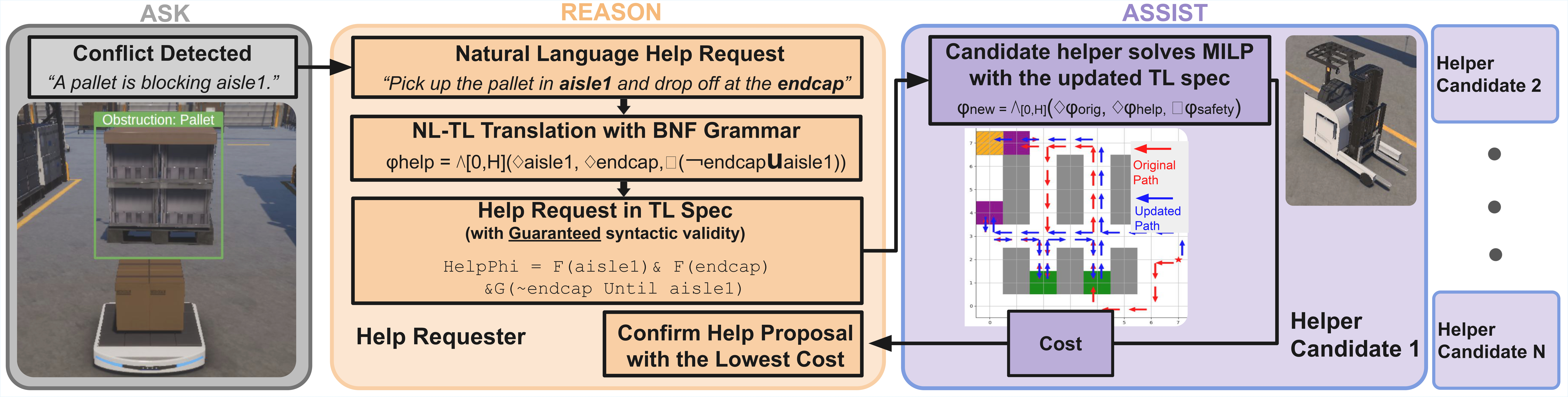
The process begins when a robot detects a conflict and uses a Large Language Model (LLM) to decide whether external assistance is required. If so, it crafts and broadcasts a natural language (NL) help request.
Potential helper robots reason over the request and respond with offers of assistance, including information about the effect on their ongoing tasks. Helper reasoning is implemented via an LLM grounded in Signal Temporal Logic (STL) using a Backus-Naur Form (BNF) grammar, ensuring syntactically valid NL-to-STL translations, which are then solved as a Mixed Integer Linear Program (MILP).
Finally, the requester robot selects a helper by reasoning over the expected increase in system-level total task completion time.
We evaluated our framework through experiments comparing different helper-selection strategies and found that considering multiple offers allows the requester to minimize added makespan.
Our approach significantly outperforms heuristics such as selecting the nearest available candidate helper robot, and achieves performance comparable to a centralized “Oracle” baseline but without heavy information demands.
Our method translates natural language to temporal logic with improved accuracy and guaranteed syntactic validity with grammar constrained generation.
| # Ex. | Method Variant | Validity (%) | Accuracy (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 5 | Gemma F + P + C (Ours) | 100.0 ± 0.00 | 98.98 ± 0.17 |
| F + P | 99.8 ± 0.45 | 98.98 ± 0.17 | |
| F | 99.0 ± 1.22 | 84.97 ± 8.65 | |
| GPT-4 F + P | 100.0 ± 0.00 | 62.82 ± 3.66 | |
| 20 | Gemma F + P + C (Ours) | 100.0 ± 0.00 | 97.58 ± 1.16 |
| F + P | 99.67 ± 0.01 | 97.58 ± 1.16 | |
| F | 99.60 ± 0.04 | 93.73 ± 2.40 | |
| GPT-4 F + P | 100.0 ± 0.00 | 92.73 ± 3.00 |
F = few-shot prompting, P = BNF grammar in prompt, C = BNF grammar constrained generation.
Our decentralized method tracks the centralized Oracle within 18% while significantly outperforming the distance based heuristics (B2) and hybrid approach (B3).
| Method | Time steps added to the system |
|---|---|
| Oracle ILS (B1) | 4 ± 1.5 |
| Ours | 4 ± 2.0 |
| Closest Helper (B2) | 5 ± 3.0 |
| Oracle Hybrid (B3) | 8 ± 3.0 |